Deconstructing Market Psychology - How Emotions Influence the Stock Market
Monday, November 4, 2024

Curious to know how human emotions impact financial markets? Discover how psychology can help you understand the volatile nature of the stock market.
Understanding The Psychology of Financial Markets
Numbers and data are not the only factors that drive financial markets, psychology and human emotions play a significant role in market fluctuations. However, credit should be provided where credit is due. And yes, economic indicators and financial analysis may seem like the most important variables to traders and investors, but there’s a bigger scheme at play—the irrationality of human behavior. Contrary to the common belief, although hold significance, are not the most important factor in market outcomes. Emotions, biases and crowd behavior are.
This is called market psychology, and traders, investors and financial professionals alike should understand it. Irrespective of whether you are trying to predict the next market move, or just wondering why certain stocks are going up or down, the psychology of financial markets is an important factor in deciding those trends.
In this blog, we will take a look at how market psychology affects trading decisions, and which psychological factors such as fear, greed, and herd behavior can affect your trading decision. And finally, we will discuss how you can deconstruct emotional biases to improve your trading strategies.
Psychological Factors that Influence Financial Markets
Speaking about the psychology of market investors, SNHU faculty Professor Krupa Desai said, “Understanding investors' mindsets and behaviors is an interesting and integral part of studying the stock market. Investors are often driven by emotions like fear and greed, which can lead to market anomalies and inefficiencies. While there is no direct way of predicting such behavior, understanding what drives investor psychology can help to provide deeper insights into market dynamics and help develop robust investment strategies.”
She added, “Traditional financial theories often assume that investors are rational actors who make decisions only on logical analysis. However, several factors like emotions, cognitive biases and heuristics can influence overall market sentiment. For instance, herd behavior is often witnessed in cases when IPOs are over-subscribed. In such cases, many inexperienced investors subscribe to company shares without conducting sufficient research and rather rely on what their friends, families and other acquaintances have to say.”
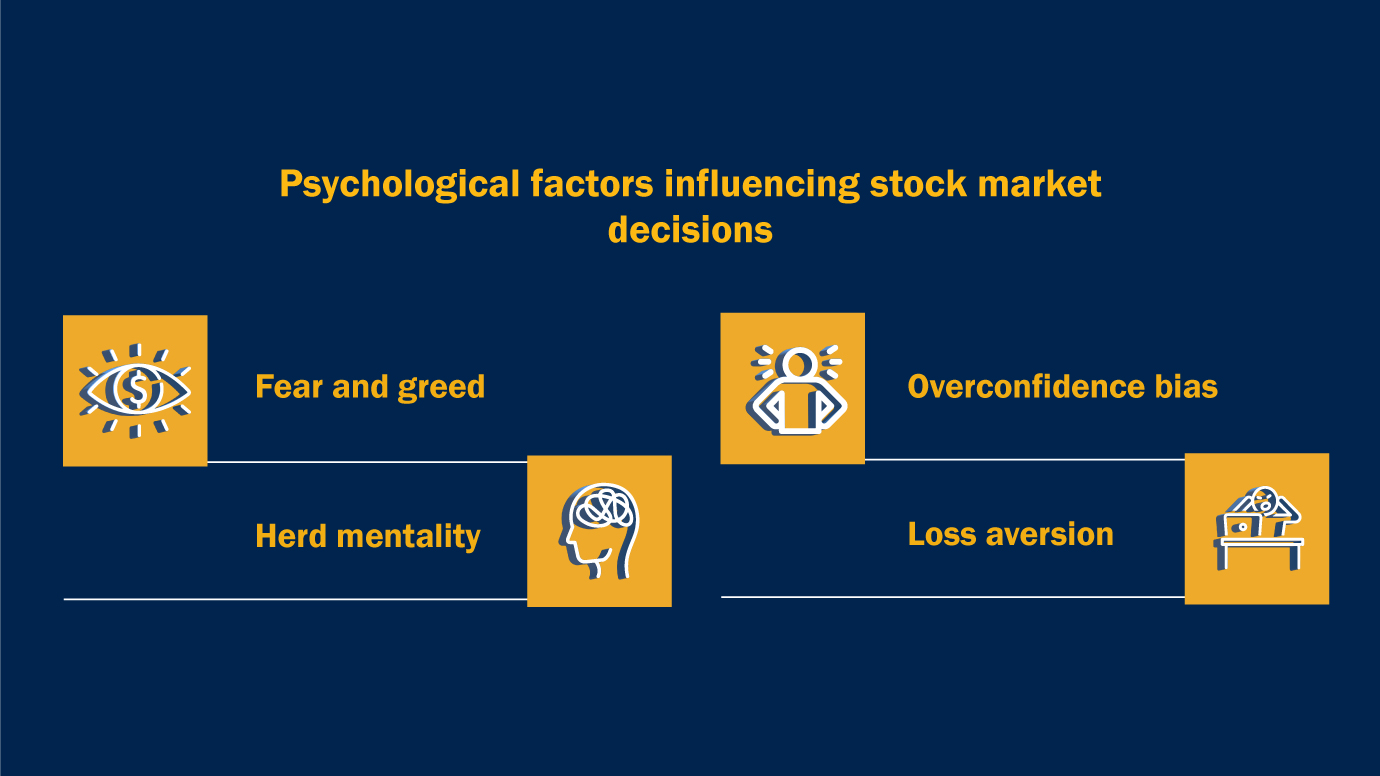
There are many psychological factors that influence financial market decisions, which result in irrational behavior and unexpected market movements. Let’s explore some of the most significant ones:
Fear and Greed: These two emotions are the engines that drive market behavior. Investors are pushed to chase profits by greed, and through fear can sell in panic during downturns. Greed is a great enabler to reckless behavior, and the movie The Wolf of Wall Street is a perfect example. In the movie, the protagonist’s rise in the financial world is built on manipulating investors’ emotions, in response to which they are seen taking impulsive and risky decisions, and finally catastrophically failing.
Herd Mentality: Investors tend to follow the crowd, assuming that if a bunch of people are doing something, that must be the right thing to do. That leads to herd mentality, where people give up their own research or instinct to follow whatever the market is doing. We saw this in 2007 with the Stock market crash, when the fear of loss caused panic selling, which only added to the market’s downward spiral.
Overconfidence Bias: During market booms, many of the traders and investors tend to overestimate their own knowledge and ability. As a result, they tend to take excessive risk, because they perceive themselves less prone to making mistakes. Day traders tend to see this bias in that they think they can beat the market based on success in the short term, and then suffer huge losses when the market corrects.
Loss Aversion: Psychologically, loss aversion is the tendency to prefer and prioritize avoiding loss instead of making a similar profit margin. This often leads us to hang on to losing stocks too long or sell winning stocks too early in financial markets, out of fear of losing profits.
Stock market history shows that these psychological factors frequently override rational decision-making, leading to volatile market conditions.
Understand the mind behind the market. Start your journey with an online MS in Psychology. Apply now.
Stock Market Psychology: The Role of Emotions in Trading
Looking at Markets Through the Lens of Behavioral Finance
Market Psychology in Trading: Strategies to Manage Emotional Biases
How an MS in Psychology Can Enhance Your Understanding of Market Behavior
If you want to study psychological principles in a deeper sense, professionals in finance can learn a lot about how emotions, biases and cognitive processes affect market behavior.
The MS in Psychology can equip finance professionals with a toolkit to comprehend investor behavior better, anticipate market trends from a behavioral perspective, and manage their own feelings in the investment world. The psychology and finance intersection is becoming a popular area of interest, and those who have expertise in both fields have a strong advantage in finding success in positions that require a thorough understanding of market psychology.
Want to understand the psychology behind market behavior? Earn an MS in Psychology degree from one of the largest US accredited universities. Get in touch with us to know more.
